The Nouns Builder Protocol
The Nouns Builder Protocol is an open-source smart contract system that allows anyone to launch a fully onchain DAO with programmable governance, automated token issuance, and treasury management. This section breaks down how the protocol works, its architecture, and how to interact with it.
How It Works
Section titled “How It Works”Token Auction Mechanisms
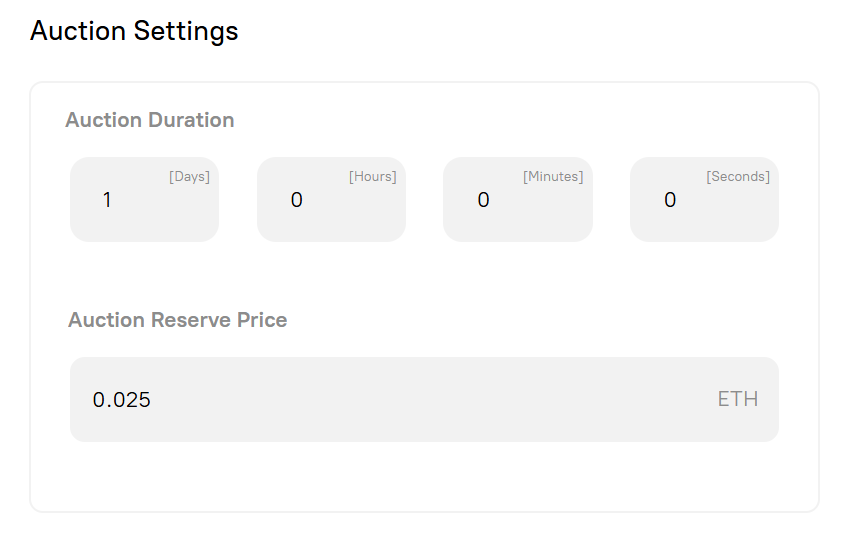
Section titled “Token Auction Mechanisms”At the heart of every Builder DAO is a recurring token auction system. Instead of launching all governance tokens at once, new tokens are auctioned one at a time on a fixed schedule.
Key characteristics:
- Auction Interval: Each DAO configures how often a new token is auctioned (e.g., every 24 hours).
- Bidding Process: Participants bid using ETH, and the highest bidder wins the token. A new high bid within the last 5 minutes of the auction will extend the auction duration for another 5 minutes. This will continue until the auction goes 5 minutes without a new high bid and the auction closes.
- Token Minting: Settling an auction distributes the last token to the winner, mints the next token, and kicks off a new 24 hour auction.
This approach ensures fair distribution over time and creates a predictable funding stream for the DAO treasury.
Governance Parameters
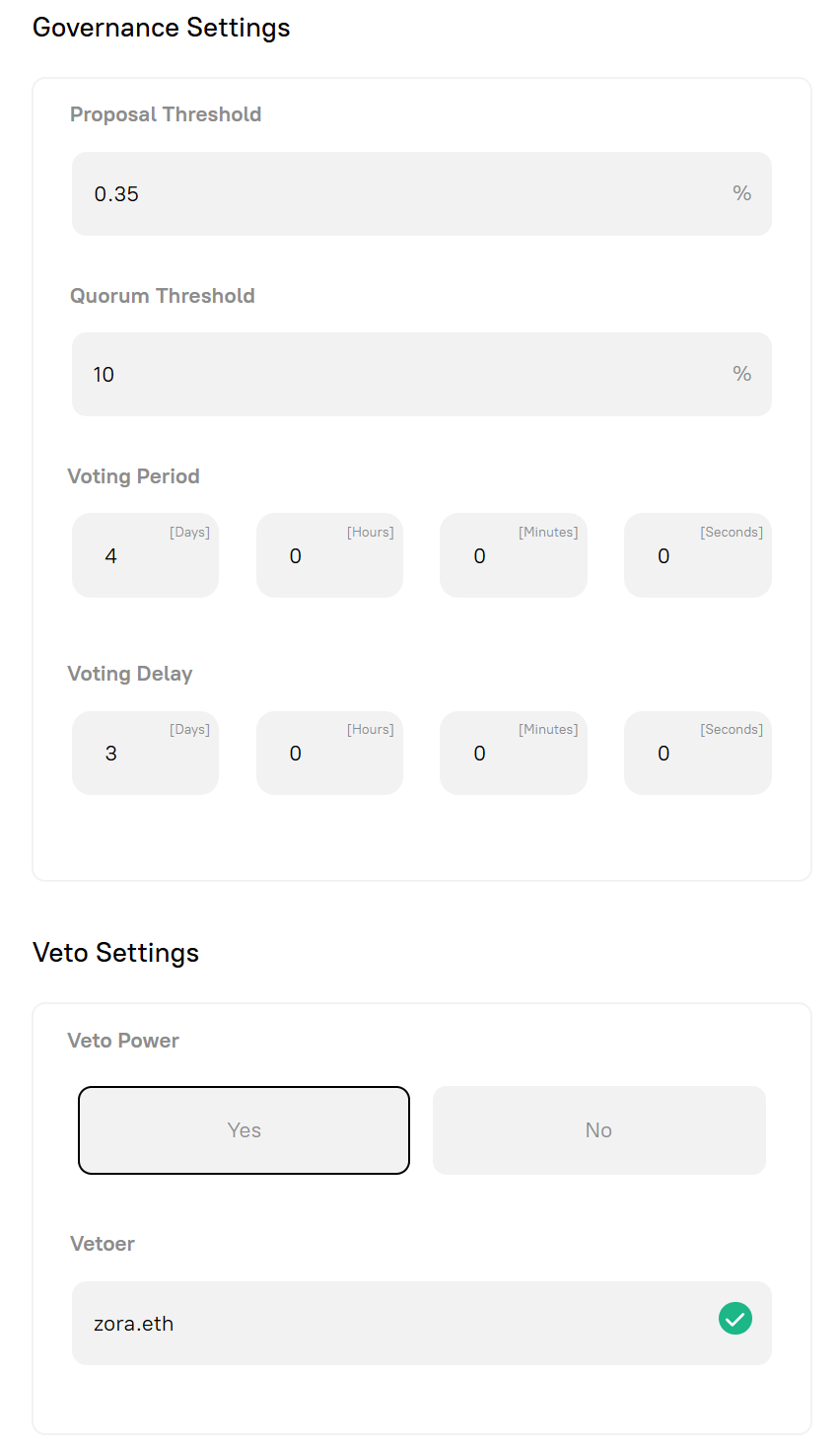
Section titled “Governance Parameters”Builder DAOs use onchain governance to make decisions. The protocol provides customizable governance settings when launching a DAO:
- Voting Delay: Time between when a proposal is submitted and when voting begins.
- Voting Period: Duration the community has to vote on a proposal.
- Quorum Threshold: Minimum number of votes needed for a proposal to be valid.
- Proposal Threshold: Minimum number of tokens required to create a proposal.
These parameters shape how responsive, secure, and participatory your DAO will be.
Treasury Management
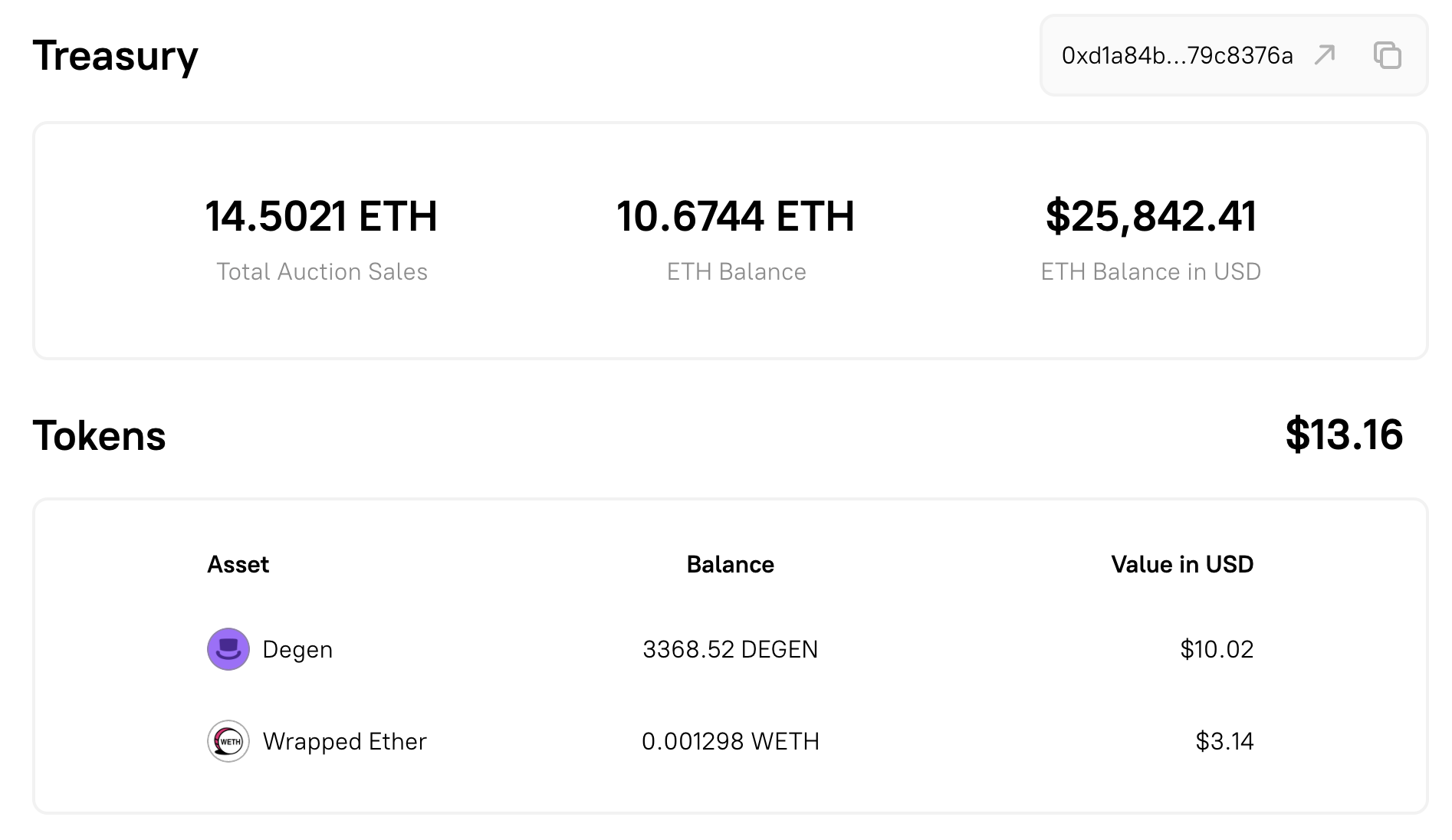
Section titled “Treasury Management”Funds from each token auction are automatically routed to the DAO’s treasury, which is controlled by governance.
- No central ownership: The treasury is owned and managed by the DAO itself.
- Proposal-controlled spending: Members propose and vote on how funds are used.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded onchain and visible to the public.
DAOs often use these funds for grants, contributor payments, community tools, or protocol improvements.
Contract Architecture
Section titled “Contract Architecture”Key Smart Contracts and Their Roles
Section titled “Key Smart Contracts and Their Roles”The Nouns Builder Protocol consists of several modular smart contracts. These include:
- Auction Contract: Manages the auction logic and token minting.
- Token Contract (ERC-721 or ERC-20): Represents ownership and governance power.
- Governor Contract: Handles proposal creation, voting, and execution.
- Metadata/Render Contract: Controls visual and metadata logic for NFTs (if using NFTs).
- Treasury Contract: Stores and secures the DAO’s funds.
Each component is interoperable and can be extended or customized by developers.
Upgradeability and Modularity
Section titled “Upgradeability and Modularity”The protocol is designed with flexibility in mind:
- Upgradeable Governance Contracts: Using the OpenZeppelin upgrade pattern, governance logic can evolve over time.
- Modular Design: DAOs can replace or extend individual components (e.g., custom token logic or auction formats).
- Parameter Tuning: Governance can change auction intervals, governance rules, and more post-launch.
This makes the protocol suitable for both simple and highly customized DAO setups.
Security Model
Section titled “Security Model”Security is paramount for onchain governance systems. Key features include:
- Immutable Treasury Ownership: Only proposals passed by token holders can move treasury funds.
- Audit History: The protocol builds on audited components from Nouns and OpenZeppelin.
- Permissionless Deployments: Anyone can deploy without relying on a central admin.
DAOs should still conduct additional audits if they customize or extend the system.
Interacting with the Protocol
Section titled “Interacting with the Protocol”Frontend Options
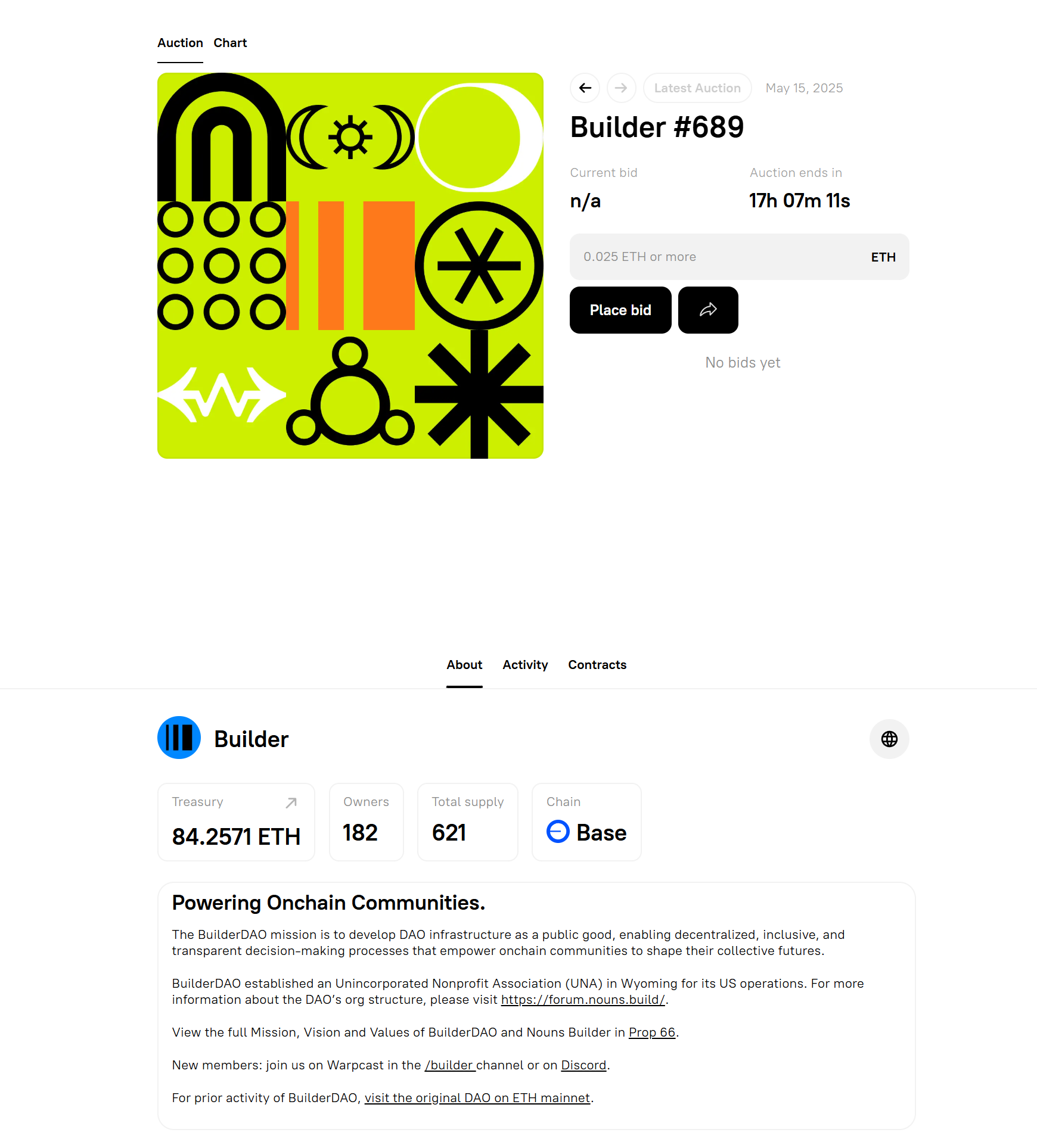
Section titled “Frontend Options”The easiest way to interact with the protocol is through the nouns.build web interface.
From the dashboard, you can:
- Launch a DAO
- View and bid on auctions
- Submit and vote on proposals
- Monitor treasury and DAO activity
Using the Builder SDK and API
Section titled “Using the Builder SDK and API”For developers, the Builder SDK offers tools to build and interact with DAOs programmatically.
Features:
- Fetch auction data and governance states
- Submit transactions via script
- Integrate DAO data into custom apps
Example Use Cases:
- Custom frontend for your DAO
- Proposal automation tools
- Onchain analytics dashboards
CLI Tools and Third-Party Integrations
Section titled “CLI Tools and Third-Party Integrations”In addition to the SDK, you can use command-line tools and third-party platforms:
- Hardhat/Foundry: For deploying and testing DAO contracts
- Tally.xyz: Some DAOs integrate with external governance dashboards
- Dune Analytics: Track DAO performance using community dashboards
- Gnosis Safe & Zodiac: Extend DAO control with multisig integrations