Governance
Creating a Proposal, Voting, and Vetoing
The Governance contract is in charge of maintaining order within the DAO. It keeps a record of proposals and votes. While the Treasury contract is in charge of holding DAO funds and executing transactions for passed proposals.
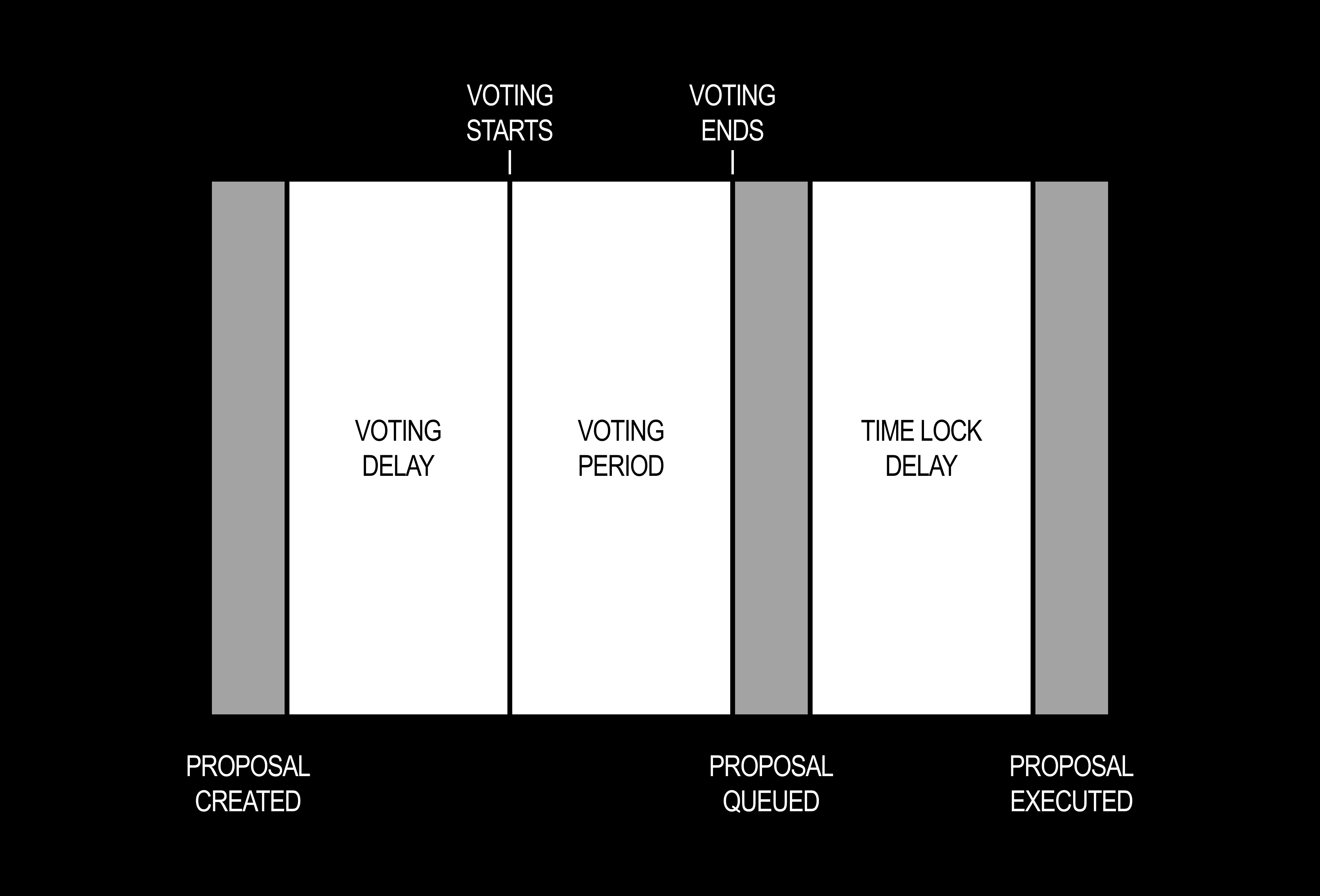
Proposal Threshold:Min BPS of total votes (NFTs) needed to put a proposal to a vote. For example, if the Proposal Threshold is set to 100 BPS and there are 500 total NFTs minted then 5 NFTs need to approve the proposal for it to a vote.Quorum Threshold:Min BPS of total For votes (NFTs) required for a proposal to passVoting Delay:The amount of time before a proposal can start voting in seconds.Voting Period:The duration for voting on a proposal in seconds.Time Lock Delay:The amount of time a successful proposal must wait between being queued and executed.
Proposal Lifecycle:
- A proposal is submitted to the DAO on-chain by an address that owns enough NFTs to clear the Proposal Threshold.
- The proposal can’t be voted on until after the voting delay time has passed.
- Once the delay period has passed, the proposal must then receive more For votes than Against and the number of For votes must meet or the Quorum Threshold.
- Finally, if the voting period has finished and it has received enough For votes then the proposed transaction is queued for execution.
- Then the proposal must pass the Time Lock Delay which defaults to 2 days.
- Finally, once the time lock has ended the proposal is then executed.
Min and Max Values
As a precaution, Nouns Builder has put guards in place to make sure that governance can’t set voting parameters to unreasonable values. Listed below are the min and max values possible for each governance parameter.
Proposal Threshold
MIN_PROPOSAL_THRESHOLD_BPS:1MAX_PROPOSAL_THRESHOLD_BPS:1000
Quorum Threshold
MIN_QUORUM_THRESHOLD_BPS:200MAX_QUORUM_THRESHOLD_BPS:2000
Voting Delay
MIN_VOTING_DELAY:1 secondsMAX_VOTING_DELAY:24 weeks
Voting Period
MIN_VOTING_PERIOD:10 minutesMAX_VOTING_PERIOD:24 weeks
Proposing
Anyone can create a proposal, however, the proposal needs to have a certain number of NFTs backing it (Proposal Threshold) before it is put to a vote.
/// @param _targets The target addresses to call/// @param _values The ETH values of each call/// @param _calldatas The calldata of each call/// @param _description The proposal descriptionfunction propose( address[] memory _targets, uint256[] memory _values, bytes[] memory _calldatas, string memory _description) external returns (bytes32)Voting
Once a proposal has received enough backing to surpass the Proposal Threshold and enough time has passed for the Voting Delay, then the voting process can begin. There are different ways to cast a vote for a proposal.
Note, the Token contract checkpoints the timestamp every time the NFT is transferred. As a result, an NFT is not able to vote on a proposal if it has been transferred after the proposal was created.
castVote
/// @param _proposalId The proposal id/// @param _support The support value (0 = Against, 1 = For, 2 = Abstain)function castVote(bytes32 _proposalId, uint256 _support) external returns (uint256) { return _castVote(_proposalId, msg.sender, _support, "");}castVoteWithReason
/// @notice Casts a vote with a reason/// @param _proposalId The proposal id/// @param _support The support value (0 = Against, 1 = For, 2 = Abstain)/// @param _reason The vote reasonfunction castVoteWithReason( bytes32 _proposalId, uint256 _support, string memory _reason) external returns (uint256)castVoteBySig
/// @notice Casts a signed vote/// @param _voter The voter address/// @param _proposalId The proposal id/// @param _support The support value (0 = Against, 1 = For, 2 = Abstain)/// @param _deadline The signature deadline/// @param _v The 129th byte and chain id of the signature/// @param _r The first 64 bytes of the signature/// @param _s Bytes 64-128 of the signaturefunction castVoteBySig( address _voter, bytes32 _proposalId, uint256 _support, uint256 _deadline, uint8 _v, bytes32 _r, bytes32 _s) external returns (uint256)Executing a Proposal
If a proposal has received a majority For vote and has passed the Quorum Threshold it can be executed on-chain. The execute function is called on the Governance contract, but forwards the calldata to the Treasury contract.
/// @param _targets The target addresses to call/// @param _values The ETH values of each call/// @param _calldatas The calldata of each call/// @param _descriptionHash The hash of the description/// @param _proposer The proposal creatorfunction execute( address[] calldata _targets, uint256[] calldata _values, bytes[] calldata _calldatas, bytes32 _descriptionHash, address _proposer) external payable returns (bytes32)Delegation
The Token contract allows holders to be able to delegate their voting power to another address. Note, on transfer the Token contract resets all delegation records.
delegate
/// @notice Delegates votes to an account/// @param _to The address delegating votes tofunction delegate(address _to) externaldelegateBySig
/// @notice Delegates votes from a signer to an account/// @param _from The address delegating votes from/// @param _to The address delegating votes to/// @param _deadline The signature deadline/// @param _v The 129th byte and chain id of the signature/// @param _r The first 64 bytes of the signature/// @param _s Bytes 64-128 of the signaturefunction delegateBySig( address _from, address _to, uint256 _deadline, uint8 _v, bytes32 _r, bytes32 _s) externalVetoing
Vetoing is an optional setting that can be configured by the founders when deploying. Note, veto power is encouraged due to the small number of votes (NFTs) at the beginning of a DAO. The veto can later before removed by the founders once the NFTs have become sufficiently decentralized.
Vetoing Proposal
/// @notice Vetoes a proposal/// @param _proposalId The proposal idfunction veto(bytes32 _proposalId) externalUpdating and Removing Veto
/// @notice Updates the vetoer/// @param newVetoer The new vetoer addressfunction updateVetoer(address newVetoer) external;
/// @notice Burns the vetoerfunction burnVetoer() external;